- Home
- Impact
- System Architecture
- PGO, Algorithms, and Optimization
- Application Layer (Demos)
- Data Collection and Validation
- Software Engineering
- Location-Aware Applications
- Final Report
6. SWE Structure, Packages etc.
Our system is built on a robust and modular software architecture that is designed for scalability and ease of use.
Publish-Subscribe Architecture
We use a publish-subscribe (pub-sub) architecture based on MQTT for communication between the UWB anchors and the central processing unit. This decoupled approach allows for a flexible and scalable system where anchors can be added or removed without affecting the overall system. The use of MQTT also allows for a high degree of interoperability.
The following UML diagram illustrates the MQTT communication between the different processes:
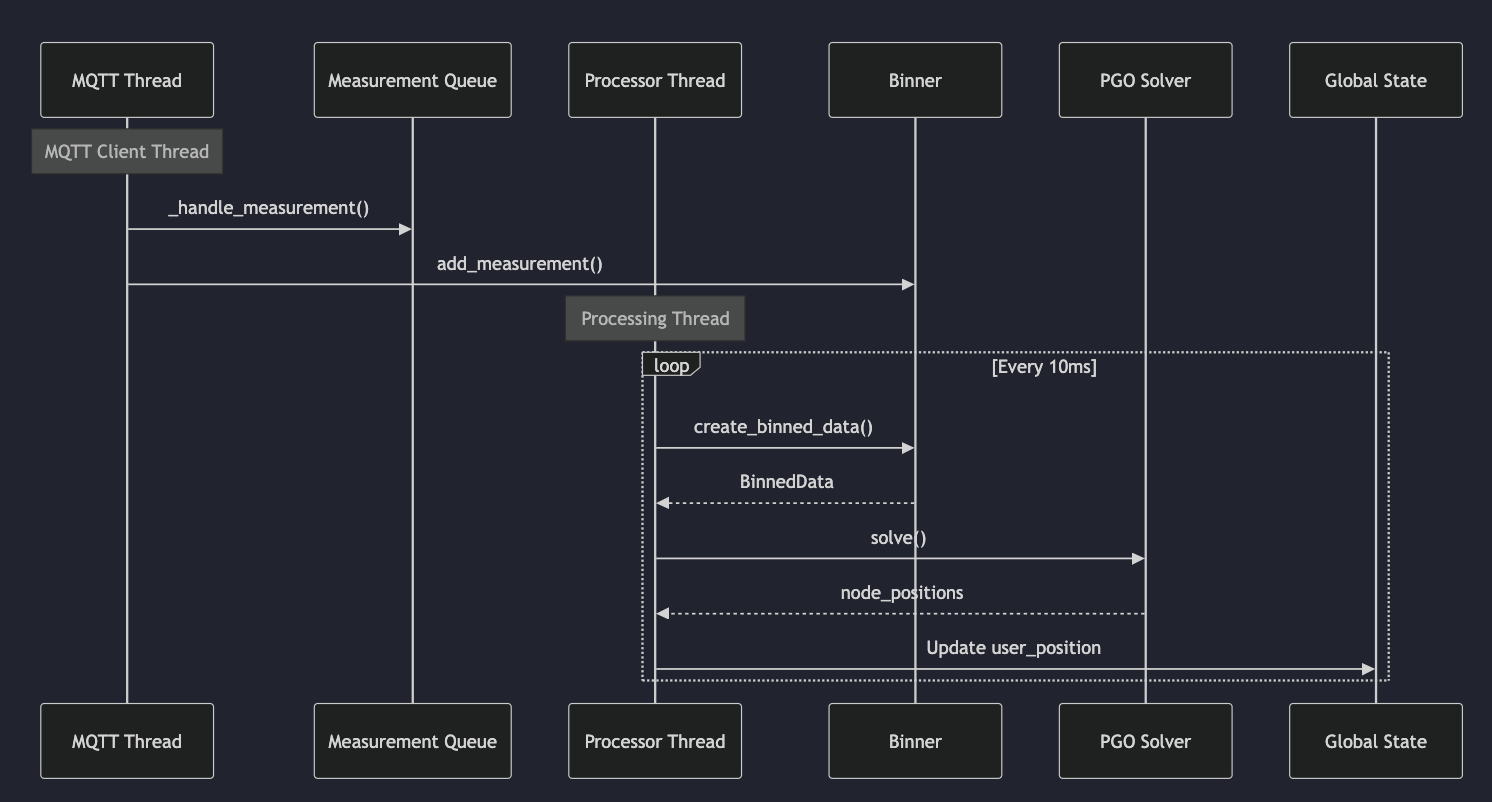
Modular Design
The entire system is designed in a way that it is easy to extend. The core functionalities are divided into three distinct layers:
- Hardware Layer: Interacts with the UWB hardware. This layer is responsible for configuring the UWB modules and reading the raw sensor data.
- Communication Layer: Handles data transfer using MQTT. This layer is responsible for publishing the sensor data from the anchors and subscribing to it on the central processing unit.
- Processing Layer: Performs the PGO calculations and other optimizations. This layer is where the magic happens. It takes the raw sensor data from the communication layer and turns it into a high-precision location estimate.
Python Packages
We have packaged the core functionalities of our system into easy-to-use Python packages. This allows developers to quickly integrate our localization middleware into their own applications with just a few lines of code. The packages are designed to be side-effect free and simple to use.
Here’s an example of how to bring up the system:
# Configure MQTT with your laptop's IP
mqtt_config = MQTTConfig(
broker="192.168.68.66", # Replace with your laptop's IP
port=1884
)
# Start server
server = ServerBringUp(
mqtt_config=mqtt_config,
window_size_seconds=1.0
)
try:
server.start()
print("Server started. Waiting for anchor connections...")
while True:
if server.user_position is not None:
print(f"Current position: {server.user_position}")
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
server.stop()
This simple and intuitive API makes it easy for developers to focus on building their applications without having to worry about the complexities of the underlying localization technology.